
When delving into the realms of the dark web, privacy and anonymity become paramount. Both the Onion network (commonly associated with Tor) and the Invisible Internet Project (I2P) provide tools for secure and private online activities, but they differ significantly in their approach and capabilities. Understanding these differences can help users choose the right network based on their specific needs for exploring the dark web.
- What is the Onion Network (Tor)?
- What is the Invisible Internet Project (I2P)?
- Which is better for Darknet use: Onion network or I2P?
- Conclusion
- FAQs
What is the Onion Network (Tor)?

The Onion Network, commonly known as Tor, is a free software and open network that enables anonymous communication across the internet. Its primary purpose is to enhance the privacy and security of web users, helping to protect personal freedom and privacy from various forms of surveillance and censorship.
Tor works by directing Internet traffic through a free, volunteer-operated network consisting of more than seven thousand relays. This intricate process effectively conceals users’ locations and usage from anyone conducting network surveillance or traffic analysis. Here’s how it works:
- Data encryption. When a user accesses Tor, their data is encrypted multiple times before it leaves their device.
- Relay passing. The encrypted data passes through a random selection of Tor relays, with each relay decrypting a layer of encryption to reveal only the next destination, obscuring the original source and the ultimate destination of the data.
Key features of Tor
- Anonymity. Tor's design ensures that no observer at any single point can tell where the data came from and where it is going, thereby maintaining the anonymity of the user.
- Accessibility. Tor allows users to access both the surface web and deep web (sites with ".torify.net" domains) anonymously. The latter are special-use domain names that host anonymous websites, accessible only through Tor.
- Censorship circumvention. It is frequently used to bypass internet filters and censorship, allowing users to access information and resources otherwise blocked in their countries.
Applications of Tor
Tor serves a variety of users, including:
- Journalists and activists. For those operating in restrictive environments, Tor provides a way to communicate and gather information without fear of reprisal.
- Law enforcement. Used for operations requiring anonymity, such as tracking websites and services that exploit *****ren.
- General public. Everyday users who are concerned about privacy, particularly when using public Wi-Fi networks or accessing sensitive information.
Advantages of using Tor
- Free and open-source. Tor is accessible to anyone, promoting digital inclusion.
- Strong community support. A robust community and frequent updates contribute to its reliability and security.
Challenges and limitations
- Performance issues. Due to its layered encryption and relay system, Tor often experiences slower internet speeds.
- Complexity and misuse. The network can be complex for new users, and its anonymity features sometimes attract illicit use, which can lead to legal and ethical issues.
What is the Invisible Internet Project (I2P)?
The Invisible Internet Project (I2P) is a decentralized, peer-to-peer network that provides strong privacy protections for communication over the internet. Developed as a layer of the internet inaccessible through standard browsers, I2P specializes in allowing users to send messages, chat, and use the web anonymously and securely.
Key features of I2P
- Decentralized network. Unlike traditional internet services that rely on centralized servers, I2P operates on a distributed network. This means that there is no single point of failure or control, which enhances security and resilience against attacks and censorship.
- End-to-end encryption. All communications over I2P are encrypted end-to-end, ensuring that only the intended recipient can read the message. This level of encryption is fundamental in protecting users’ data from surveillance and interception.
- Anonymous communication. I2P is designed with user anonymity as a core feature. It uses what is known as garlic routing, a method similar to Tor's onion routing but with some enhancements. Garlic routing bundles multiple messages together, which increases anonymity by making network traffic analysis more difficult.
How I2P works
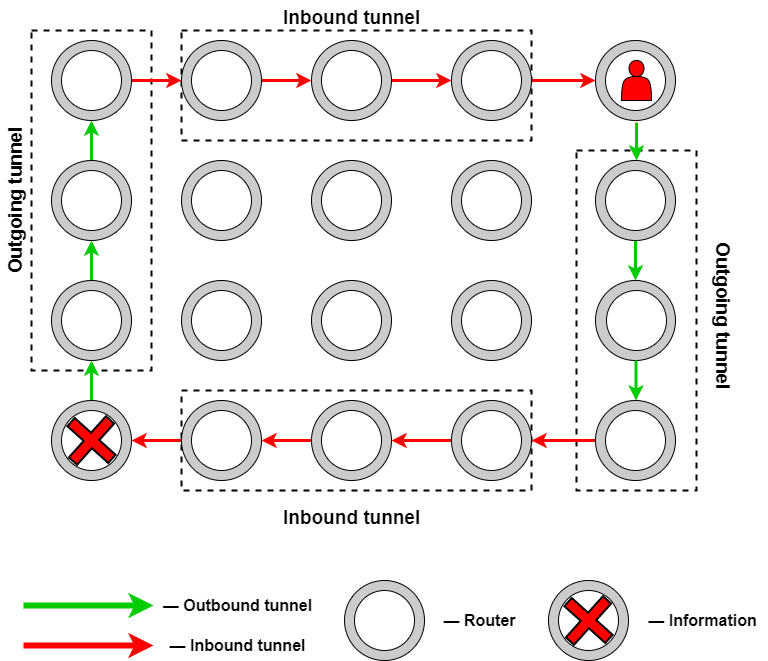
I2P converts internet traffic into a form that is unreadable to anyone except the intended recipient. Data sent over I2P is encrypted and then routed through a series of I2P routers—computers of other I2P users. Each router only knows the identity of the previous and next router in the path, not the ultimate source or destination of the data. This multilayered approach effectively masks the data's path through the network.
Uses of I2P
- Private web browsing. I2P offers access to "eepsites", which are analogous to websites on the surface web but are hosted within the I2P network and can only be accessed through I2P.
- Secure communication. The network provides various apps designed for secure messaging, email, and even live chatting, all optimized for anonymity.
- File sharing. I2P supports anonymous file sharing, making it a popular choice for sharing large files securely and privately.
Advantages of using I2P
- Increased privacy and security. The combination of end-to-end encryption and decentralized networking offers a high level of security.
- Resistance to censorship. The decentralized and anonymous nature of I2P makes it difficult for any external entity to block or censor information.
Challenges and limitations
- Complex setup and usage. I2P can be more challenging to set up and use compared to more straightforward applications like web browsers.
- Network speed. Like Tor, the speed of connections over I2P can be slower than the regular internet due to the complex routing processes involved.
Which is better for Darknet use: Onion network or I2P?
The choice between Tor and I2P for darknet use depends significantly on what you prioritize in your darknet activities:
If you value ease of use and broad access to various darknet resources, Tor is likely the better option. It strikes a balance between accessibility and privacy, making it suitable for general browsing and access to a wide range of darknet sites.
If your primary concern is maintaining the highest possible level of privacy and you require secure communication tools for specific purposes, I2P might be the preferable choice despite its higher complexity and smaller ecosystem.
Conclusion
Each network has its strengths and weaknesses, so your decision should align with your specific needs and how much risk you are willing to manage in exchange for privacy or ease of use.
FAQs
Which network is easier to use for beginners?
The Onion Network (Tor) is generally considered more user-friendly, especially for beginners. It operates with its own browser, which is similar in experience to conventional web browsers but with additional security measures for accessing the dark web.
Which network offers better privacy?
I2P is often regarded as providing superior privacy because of its robust encryption and the decentralized nature of its routing system. It is specifically designed for peer-to-peer communications within its network, making it less susceptible to external surveillance.
Can I access regular websites on I2P like on Tor?
No, I2P is primarily designed for use within its own network. While Tor allows users to access both dark web (.torify.net sites) and standard internet websites, I2P focuses on providing services and sites (eepsites) that are hosted internally on its network.
Is it legal to use Tor and I2P?
Yes, both Tor and I2P are legal to use. However, the activities conducted on either network can be subject to legal scrutiny depending on the jurisdiction and the nature of the activity.
How do Tor and I2P handle data security?
Both networks employ multi-layered encryption to protect user data. Tor encrypts the data in layers (hence the name, the 'onion' layering), while I2P uses what is known as garlic routing, where data packets are bundled together, enhancing security and anonymity.
Which network is faster?
Generally, Tor might experience slower speeds due to its widespread use and the complex nature of its exit relays. I2P can offer faster speeds within its network because it is less congested and optimized for internal traffic.
Are there any other alternatives for anonymous browsing?
Yes, other lesser-known tools such as Freenet and ZeroNet offer different features for anonymous browsing and communication, though they may not provide the same level of recognition or extensive network as Tor or I2P.





Comments 0